Common Difficulties in Foam Control and How to Conquer Them Efficiently
Effective Strategies for Attaining Optimum Foam Control in Chemical Production
Effective foam control is an essential facet of chemical manufacturing that can substantially influence manufacturing performance and product top quality. By comprehending the systems of foam formation and selecting proper anti-foaming representatives, manufacturers can take positive measures to mitigate too much foam.
Comprehending Foam Formation

Surfactants, or surface-active agents, reduce the surface area stress of the fluid, assisting in bubble stability and promoting foam generation. Furthermore, frustration or blending processes can enhance bubble formation, frequently exacerbating foam issues. The qualities of the liquid medium, including thickness and density, further influence foam behavior; as an example, more viscous fluids often tend to catch air much more effectively, resulting in increased foam stability.
Recognizing these essential aspects of foam development is important for efficient foam control in chemical manufacturing. By acknowledging the conditions that promote foam advancement, makers can implement targeted strategies to minimize its adverse results, consequently maximizing production procedures and ensuring constant product quality. This foundational knowledge is essential prior to discovering particular methods for controlling foam in industrial settings.
Option of Anti-Foaming Agents
When choosing anti-foaming agents, it is vital to take into consideration the certain qualities of the chemical procedure and the kind of foam being produced (Foam Control). Numerous variables influence the efficiency of an anti-foaming representative, including its chemical composition, temperature stability, and compatibility with various other process materials
Silicone-based anti-foams are widely utilized due to their high performance and broad temperature range. They work by reducing surface stress, permitting the foam bubbles to coalesce and break even more conveniently. They may not be suitable for all applications, especially those involving delicate solutions where silicone contamination is a concern.
On the other hand, non-silicone representatives, such as mineral oils or organic compounds, can be advantageous in specific scenarios, specifically when silicone residues are unfavorable. These representatives often tend to be less reliable at higher temperature levels yet can provide effective foam control in other conditions.
Additionally, recognizing the foam's beginning-- whether it arises from oygenation, frustration, or chemical responses-- guides the selection process. Examining under actual operating problems is crucial to make certain that the selected anti-foaming representative satisfies the distinct demands of the chemical production process successfully.
Process Optimization Methods
Reliable foam control is an important aspect of optimizing chemical manufacturing processes. To enhance effectiveness and decrease production prices, suppliers have to carry out targeted process optimization methods. One vital method entails readjusting blending speeds and arrangements. By fine-tuning these parameters, operators can lower disturbance, therefore minimizing foam formation throughout blending.
In addition, controlling temperature and stress within the system can dramatically impact foam generation. Decreasing the temperature level might reduce the volatility of particular parts, leading to reduced foam. Preserving ideal stress degrees aids in minimizing extreme gas release, which adds to foam security.
One more efficient method is the tactical enhancement of anti-foaming representatives at critical this website phases of the procedure. Mindful timing and dosage can make sure that these agents properly reduce foam without disrupting various other process parameters.
Additionally, incorporating a systematic analysis of basic material properties can help recognize inherently lathering materials, enabling preemptive actions. Lastly, performing regular audits and process evaluations can expose inefficiencies and locations for renovation, making it possible for continual optimization of foam control methods.
Tracking and Control Equipment
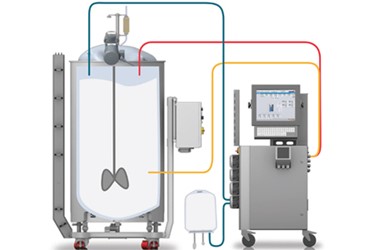
Monitoring and control systems play a critical function in maintaining ideal foam management throughout the chemical manufacturing process. These systems are vital for real-time observation and change of foam degrees, making certain that manufacturing effectiveness is made the most of while decreasing interruptions caused by excessive foam development.
Advanced sensing units and instrumentation are utilized to spot foam thickness and elevation, providing crucial information that informs control algorithms. This data-driven method enables the prompt application of antifoaming representatives, making certain that foam levels continue to be within appropriate restrictions. By incorporating surveillance systems with process control software application, makers can carry out automated feedbacks to foam fluctuations, minimizing the requirement for hands-on intervention and enhancing functional uniformity.
Additionally, the combination of device learning and anticipating analytics right into keeping track of systems can facilitate positive foam administration. By evaluating historic foam data and operational criteria, these systems can forecast foam generation patterns and advise preemptive steps. Regular calibration and upkeep of surveillance tools are vital to guarantee accuracy and reliability in foam discovery.
Inevitably, effective monitoring and control systems are important for optimizing foam control, promoting safety and security, and improving total productivity in chemical manufacturing settings.

Study and Finest Practices
Real-world applications of tracking and control systems highlight the significance of foam administration in chemical production. A remarkable case study involves a massive pharmaceutical producer that applied an automated foam detection system.
Another excellent case originates from a petrochemical business that adopted a combination of antifoam agents and process optimization strategies. By assessing foam generation patterns, the company customized its antifoam dosage, causing a 25% decrease in chemical usage and substantial price savings. This targeted technique not only reduced foam interference however additionally enhanced the Read Full Report general stability of the manufacturing process.
Verdict
In conclusion, achieving optimum foam control in chemical production necessitates a detailed method encompassing the option of appropriate anti-foaming agents, application of procedure optimization methods, and the integration of sophisticated monitoring systems. Routine audits and training even more enhance the effectiveness of these techniques, fostering a culture of continuous improvement. By dealing with foam formation proactively, manufacturers can dramatically improve production efficiency and item top quality, eventually adding to more cost-effective and lasting operations.
By recognizing the mechanisms of foam development and choosing appropriate anti-foaming representatives, makers can take aggressive procedures to alleviate too much foam. The qualities of the liquid medium, including thickness and thickness, additional influence foam behavior; for instance, more viscous liquids often tend to trap air a lot more properly, leading to enhanced foam stability.
Recognizing these fundamental elements of foam development is essential for efficient foam control in chemical manufacturing. By examining historic foam data and operational specifications, these systems can anticipate foam generation patterns and advise preemptive measures. Foam Control. Regular audits of foam control determines make certain that procedures remain enhanced, while promoting a society of aggressive foam look at this site monitoring can lead to lasting improvements across the manufacturing spectrum